
As demand for bandwidth continues to explode and connectivity becomes more critical than ever, communications service providers (CSPs) often face multiple challenges in operating and maintaining the underlying network infrastructure that typically spans multiple business entities across network domains. In order to offer services to customers with geographically diverse locations, CSPs often lease resources in networks where they do not have a presence (“off net”). This enables them to provide end-to-end services to their customers, but usually involves a manual and complex negotiation process, from business arrangement to service design and activation, requiring coordination across two or more service provider networks or independent operational units within a service provider.
With today’s complex networks, there is a strong need for network automation in order to reduce some of the operational costs and enable faster service delivery, reducing time to revenue. AT&T, Orange and Fujitsu build upon a leading open-source framework known as ONAP (Open Network Automation Platform) to provide a common reference for multi-domain orchestration of optical network services. This is accomplished by leveraging a standards-based approach, through the Multi-domain Optical Network Service (MDONS) blueprint that we contributed to as part of the Frankfurt release of ONAP.
ONAP offers a comprehensive, open-source framework that delivers capabilities for the design, creation, orchestration, monitoring, and lifecycle management of VNFs, SDN networks and higher-level services that combine them. In our implementation, we leverage ONAP building blocks – A&AI, External-API, SDC, SDNC, SO, UUI – to provide an end-to-end multi-operator Layer 1 (L1) subscriber service orchestrated across inter-domain OTN links. As part of the framework, we incorporate service models based on MEF L1 definitions through TOSCA templates that are defined in SDC, which are then distributed to other ONAP components during run-time for service activation and provisioning.
Mapping multi-domain orchestration
Within service provider environments, L1 subscriber services may traverse multiple optical domains, managed by domain-specific SDN controllers, all of which need to be onboarded into the ONAP framework before end-to-end service provisioning. Through MDONS, we enable third-party SDN controller onboarding and domain management in ONAP by incorporating support for standard data models and APIs defined by both Open ROADM MSA and ONF Transport-API (TAPI). These standards-based REST APIs are integrated southbound of ONAP through SDNC and A&AI, providing CSPs the flexibility to manage SDN controllers from any vendor that supports these interfaces. We have integrated Fujitsu’s Virtuora Network Controller into ONAP and leveraged multiple instances of it, along with OpenDaylight based Transport-PCE as part of this implementation.
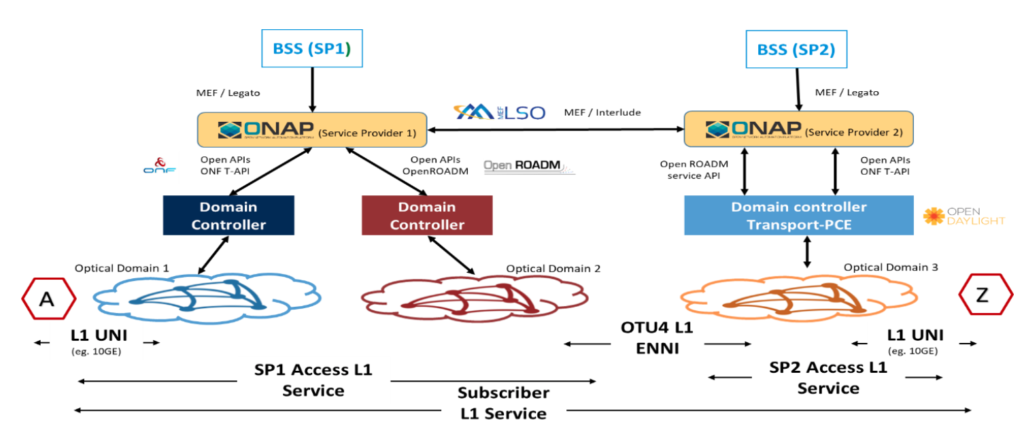
Service requests are typically instantiated by higher layer BSSs (Business Support Systems) that interact with ONAP through the External-API, which transfers the request with the corresponding endpoints into the SO component. In this implementation, we further decompose the subscriber service into the corresponding domain access services and invoke the respective optical domains controller through SDNC directed graphs (TAPI, Open ROADM etc.) to activate the service request. The workflow that MDONS describes is completely event-driven based on notifications ONAP receives regarding any status change during execution, furthering the shift towards open network automation.
Open optical networking
The ONAP MDONS blueprint is primarily aimed at reducing OPEX by automating some of the manual steps required for service provider interconnections, and may result in CAPEX savings as well, due to improved management of these interconnect points. It is applicable to any service provider offering global enterprise services, or services that otherwise extend beyond their own network resources.
By enhancing the functional capabilities of ONAP in enabling optical services, MDONS allows for the development of customized service offerings and applications suited to the specific needs of service providers in further driving network automation at the optical layer. Further details regarding the MDONS implementation can be found here.