
As Open Radio Access Network (RAN) architecture gains transformative momentum, including significant government support and funding, security is understandably a significant area of focus and concern for governments and service providers. What steps can operators and vendors take to proactively secure networks? One significant measure is to maintain a current Software Bill of Materials (SBOM), which has emerged as a key building block in software security and software supply chain risk management.
What is SBOM?
SBOM is a detailed inventory or list that documents all the software components used in a particular software application, system, or product. Think of it as a list of ingredients for a recipe, or a parts list for assembling a product. SBOM provides a comprehensive overview of the software’s composition, including its dependencies, libraries, open-source components, and version or release information.
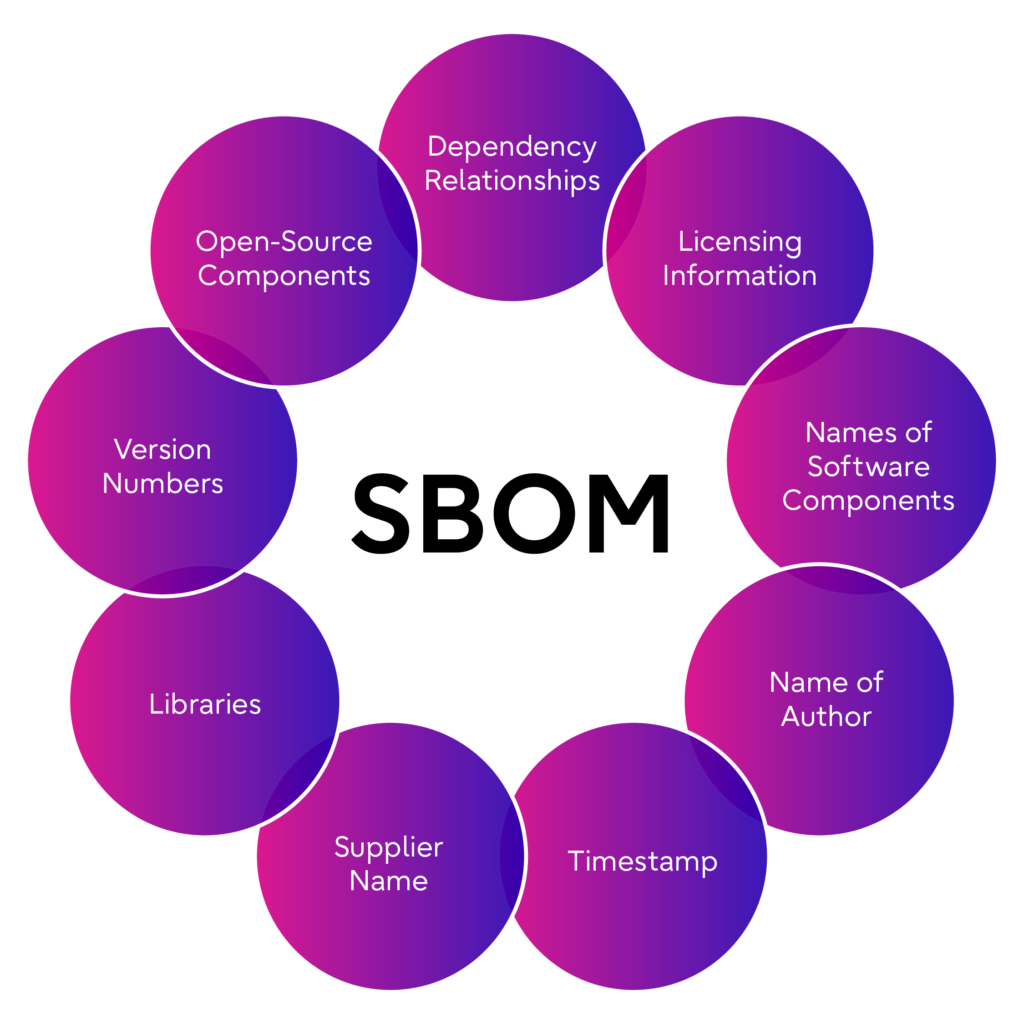
Image caption: Essential SBOM components
SBOM primary purpose
The primary purpose of an SBOM is to enhance transparency and improve security and compliance in software development and supply chain management. SBOM enables organizations to identify and track the software components they use, which is particularly crucial in modern software development that often involves a combination of proprietary code and open-source libraries from various entities. Similar to a bill of materials (BOM) for supply chain and manufacturing, it tracks most software packages’ extensive third-party components. Thus, lack of systemic visibility into the composition and functionality of SBOM contributes substantially to cybersecurity risk. In a 5G Open RAN environment where multiple vendors and suppliers provide various software components, SBOM security is crucial.
SBOM security benefits
With a clear and up to date SBOM, organizations can better manage vulnerabilities, respond to security incidents, ensure license compliance, and evaluate the security posture of their software products. It also helps stakeholders, such as customers and regulators, understand the software’s composition and potential security implications. SBOM security has gained importance in various industries, especially in the context of cybersecurity and software supply chain security; it is critical in promoting transparency, enabling better risk management and building trust in the integrity and security of software products.
Securing the SBOM in a multivendor Open RAN (Radio Access Network) environment is critical to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the information contained in the SBOM.Open RAN represents a network architecture that empowers operators to integrate components from diverse vendors. Consequently, the implementation of robust security controls becomes imperative.
Reasons to implement SBOM security
Vulnerability management: The SBOM provides a comprehensive list of all software components and their versions used in the Open RAN environment. This is crucial for identifying and managing vulnerabilities effectively. Without a secure SBOM, it becomes challenging to track and remediate vulnerabilities, increasing the risk of exploitation.
Supply chain security: SBOM security enables network operators to scrutinize the sources of software components and ensure they are from trusted vendors, helping to prevent inclusion of potentially compromised or malicious components.
Third-party risk management: Open RAN often integrates solutions from different vendors. By securing the SBOM, network operators can evaluate the security posture of each vendor’s software, identify potential risks, and make informed decisions about vendor partnerships based on their security practices.
Patch management: The SBOM aids in understanding software component dependencies and interconnections, enabling operators to prioritize and apply security patches efficiently and reducing the risk of known vulnerabilities being exploited.
Compliance and regulatory requirements: Many industries have stringent regulations and compliance requirements for data privacy and security. SBOM security helps network operators demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations and standards by providing clear visibility into the software components and their security status.
Security incident response: Strong SBOM security can expedite the incident response process by enabling security teams to quickly assess impact, identify affected components, and take appropriate action swiftly.
Transparency and trust:Open RAN environments promote transparency, interoperability, and vendor diversity. A secure SBOM fosters trust among different stakeholders by providing visibility into the software components, their sources, and the security measures in place.
Continuous monitoring and assurance: SBOM security allows for continuous monitoring of software components and their security status. It aids in proactively identifying potential risks and maintaining a high level of security assurance throughout the network’s lifecycle.
Reduced attack surface: A secure SBOM helps eliminate unnecessary or outdated software components, reducing the overall attack surface and making the network more resilient against potential cyber threats.
Licensing information: It lists the licenses associated with each software component, including open-source libraries or third-party components. This helps organizations ensure compliance with licensing requirements and avoid potential legal issues related to license violations.
NTIA & DOC SBOM activities
The National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) and U.S. Department of Commerce (DOC) jointly published an article, “The Minimum Elements For a Software Bill of Material (SBOM)”, in accordance with Executive Order 14028 on improving Nation’s Cybersecurity. This article provides detailed information on SBOM and the proposed minimum elements deemed necessary to achieve the goals expressed in Executive Order 14028. They establish the baseline technology and practices for provisioning SBOMs, as summarized below.
Data fields: Baseline information about each component that should be tracked, including Supplier, Component Name, Version of the Component, Other Unique Identifiers, Dependency Relationship, Author of SBOM Data, and Time Stamp.
Automation support: Support for automation, including via automatic generation and machine readability to allow for scaling across the software ecosystem, in addition to data formats used to generate and consume SBOMs include SPDX, CycloneDX, and SWID tags.
Practices and processes: Defines the operations of SBOM requests, generation, and use, including frequency, depth, known unknowns, distribution and delivery, access control, and accommodation of mistakes.
SBOM security is fundamental to Open RAN security
Securing the SBOM in Open RAN environments is fundamental to achieving a higher level of security, enabling efficient vulnerability management, enhancing supply chain security, and meeting compliance requirements. According to the NTIA article mentioned earlier, the primary security use case for SBOM is currently focused on identifying known vulnerabilities and risks within the software supply chain.
Some developers opt to include vulnerability data within the SBOM, supported by various SBOM data formats. This approach provides clear benefits to developers. However, it is important to note that SBOM data is predominantly static, reflecting the properties of specific software as built at a given moment. On the other hand, vulnerability data is dynamic, continuously evolving over time. Software that may not have been considered vulnerable initially can become vulnerable as new bugs or vulnerabilities are discovered. The ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity elicits constant efforts by cybercriminals to discover and exploit vulnerabilities. As a result, security must remain dynamic and adaptive to counter these evolving threats.
To secure the SBOM, a baseline minimum set of security controls should be in place. But from a holistic perspective having a robust security program is essential to keep security threat vectors at bay in any network. Below is a high-level list of security controls that aligns with defense-in-depth strategy to secure SBOM in a multivendor 5G Open RAN environment from a holistic perspective.
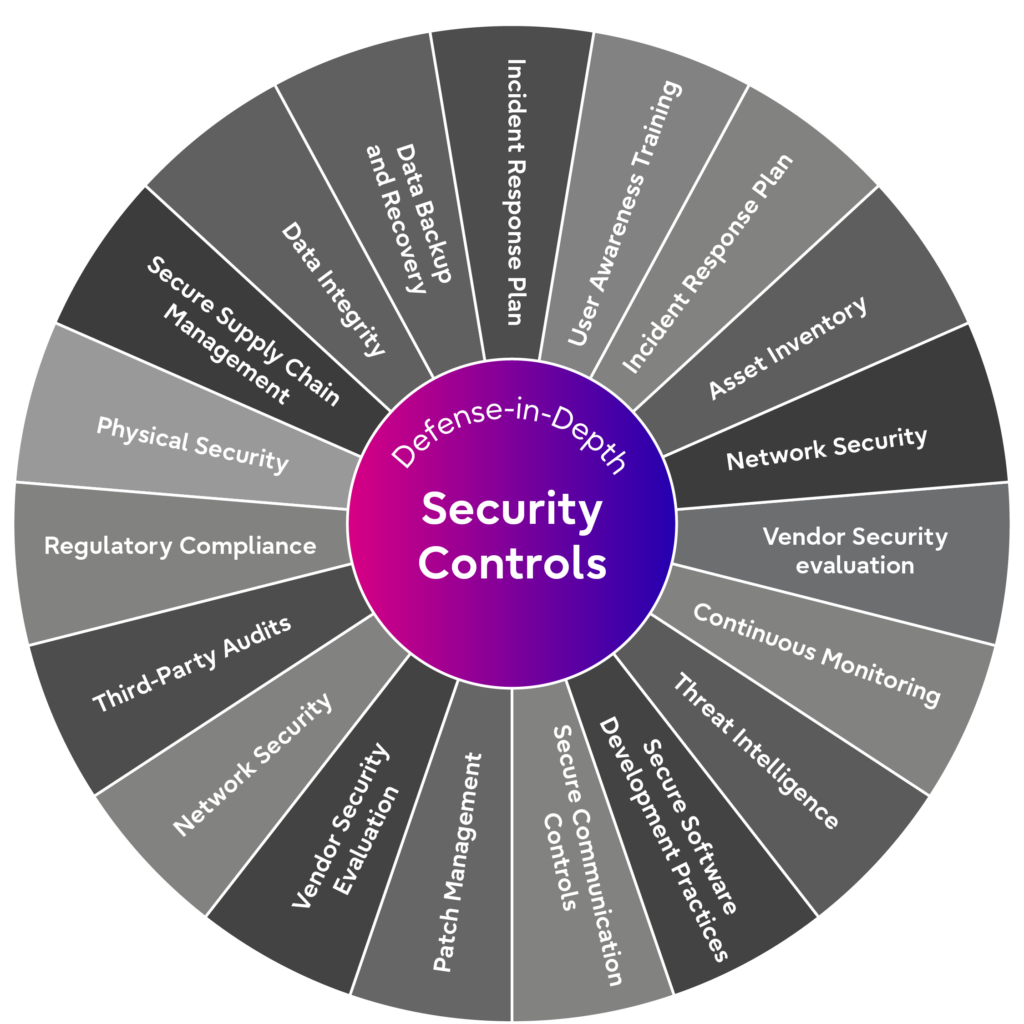
Image caption: Defense-in-Depth minimum security controls
Proactive vulnerability management
Security is an ongoing process, and it is essential to continuously monitor and update security controls to adapt to new threats and vulnerabilities as they emerge. In conclusion, safeguarding SBOM security is an essential responsibility that cannot be overlooked in today’s interconnected, dynamic digital landscape.
By implementing robust security controls, conducting thorough vendor evaluations, and adhering to best practices in supply chain management, suppliers, vendors, and operators can fortify Open RAN environments against potential threats and vulnerabilities. A proactive approach to vulnerability management, including continuous monitoring, compliance with industry standards, and alignment to defense-in-depth security strategy, will not only protect networks and data but also foster trust among stakeholders. Committing to secure SBOMs, ensuring a resilient and secure Open RAN deployment, and contributing to a safer digital ecosystem will definitely result in secure infrastructure. The SBOM is a valuable asset in modern software development and supply chain management, promoting security, transparency, and trust between all parties involved in the software’s lifecycle.